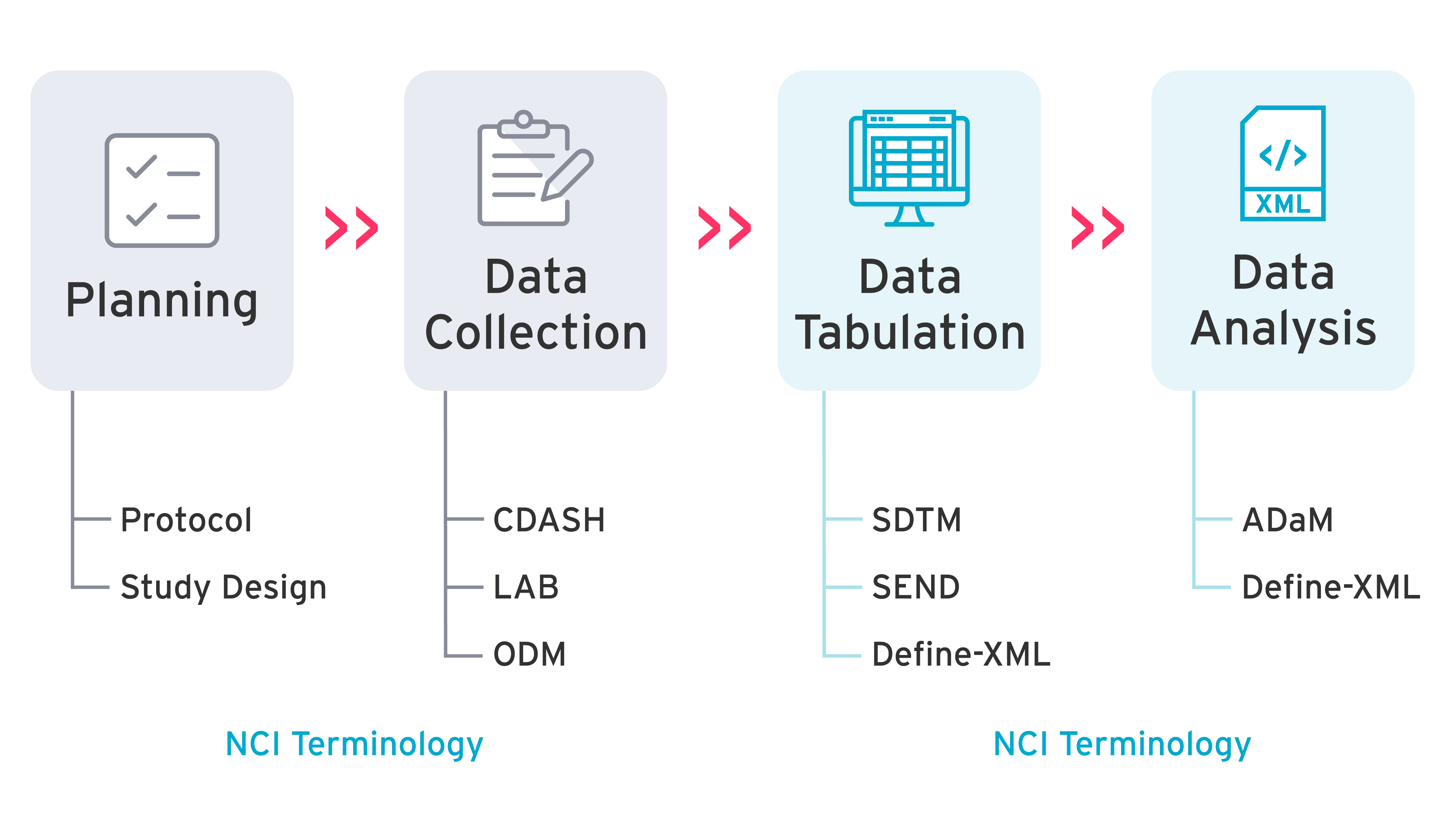
How CDISC standards fit into the drug development process.
The clinical trial process is a long, expensive, complicated one that often ends in failure. That means to have a successful outcome, careful decision making and planning are absolutely essential. This is where CDISC standards come in!
The FDA requires clinical study data to be submitted in a standardized format. This allows the FDA to receive, process, review, and archive submissions efficiently. It also lets them explore research options by putting together data from multiple studies.
As part of a collaboration with the FDA, CDISC developed data standards to be used from study design and data collection through to analysis. Implementation of these standards can be a complex and costly process. And it’s important to have an excellent understanding of these standards, along with regulatory requirements.
CDISC standards that are required for submission by the FDA:
- SEND (Standard for Exchange of Non-Clinical Data) describes a way to collect and present nonclinical data.
- SDTM (Study Data Tabulation Model) describes the contents and structure of the data collected in a clinical trial. You can read our blog on All you need to know about SDTM.
- ADAM (Analysis Data Model) describes the organization, structure, and format of analysis datasets and associated metadata. You can read our blog on 3 things you should know about ADaM standards.
- Define-XML provides the metadata for human and animal datasets using SDTM and/or SEND, and analysis datasets using ADaM. You can read our blog on How our visual define.xml editor gives you faster define!
These CDISC standards must be successfully implemented at different stages in the drug development process.
Download Now: Free guide on CDISC standards you need to know about for regulatory submission
If you want to find out more about CDISC standards, you can read our blog Introduction to CDISC standards.
Stages of drug development in clinical trials
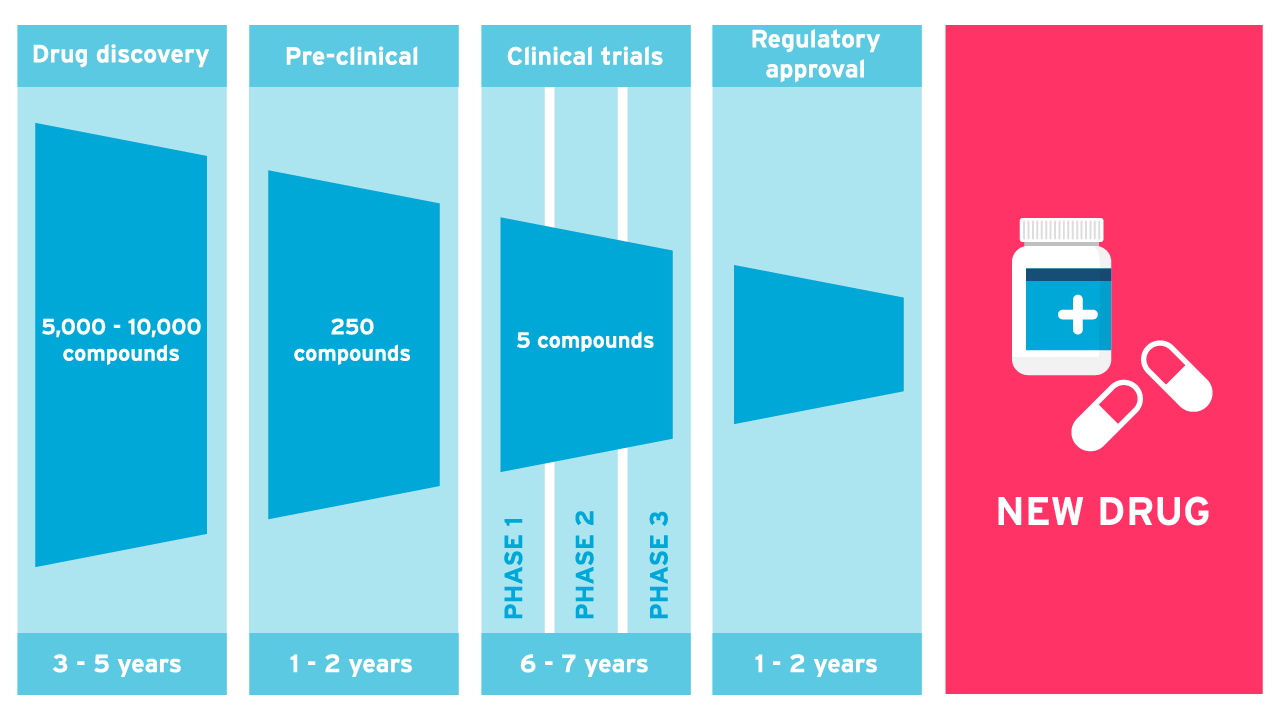
- Basic Research is carried out to discover a condition or disease to target.
- At Drug Discovery, scientists develop a chemical compound that can be used to treat the condition or disease.
- At the pre-clinical stage, the drug is tested in lab and animals to determine whether the drug is safe for humans. This evidence is presented to the FDA for approval to go ahead to Phase I.
- Phase I determines the highest dose that can be given to a subject that’s safe. If a safe dose is found then the FDA will give approval for phase II. The number of patients varies according to the drug, but there are typically 20 to 80 volunteers and is not randomized.
- Phase II determines the efficacy and side effects of the drug. If it’s found to be safe and has some benefit then approval to move to phase III will be granted. Phase II can include hundreds of patients and can last several months to 2 years.
- Phase III determines the efficacy and monitoring of adverse reactions. This phase is usually randomized, controlled, multi-centered, and provides most of the long term safety data. Thousands of patients can be tested who have the disease or condition. At this point, the study is submitted for approval to the FDA for review to release the drug into the market.
- The post-marketing surveillance (PMS) and monitoring phase occur after the drug is released in the market. It determines the safety and efficacy of real-world effectiveness for over a longer-term, and it’s not randomized.
How CDISC standards fit in
CDISC SEND and Define-XML should be implemented in the pre-clinical phase of a study. CDISC SDTM and ADaM standards should be implemented in phase I of a study and used throughout phases II and III. To do this though, detailed planning is needed right from the beginning.
To be able to implement CDISC standards effectively, it’s important to know exactly what the end deliverables are, right at the start. Ideally CDISC implementation starts with defining your tables, listings, and figures (TLF). From there define your ADaM datasets and Define-XML and SDTM datasets to eCRF design and annotations.
However, for various reasons, it’s not always possible to implement CDISC standards at the very beginning. But by having your end deliverables defined upfront, it’s easier to judge at what point in the process you can implement data standards. And it’s really important to anticipate all the problems that could crop up beforehand. This means you won’t need to waste time, later on, trying to fix issues that could have been avoided.
|
If you have a good foundation in place, that is building well-structured eCRFs, you’ll be much more successful implementing SDTM, ADaM and the development of TLF’s later on in the process. |
The benefits of using CDISC Data Standards
By establishing your standards rights from the off, it makes it much easier to connect data across different systems later on. Using data standards gives a much more efficient process for acquisition, aggregation, analysis, and reporting. You can re-use standardized metadata such as eCRFs, terminologies, datasets, etc. And with standards in place, you don’t need to reformat your data to use in different systems.
If standardized data is collected, the process is much quicker, less money is wasted and there’s much less effort needed. All those time consuming manual tasks don’t need to be done. You can build studies quickly because it’s a more efficient process. And having integrated systems just adds to this efficiency.
Additionally, by using data standards, the history of a clinical trial can be properly recorded and traced. This gives a greater insight into the development of drugs and therapeutic indications.
And if your data standards are implemented correctly, you can be confident knowing that your study complies with the FDA when the time comes for submission.
And to round off…
If this feels like a lot to take on yourself, there’s ways technology can help. For instance, there are many tools that have been developed to help make the process more efficient and effective.
The Formedix automation platform and metadata repository is one example of this. It specifically helps with phases I through to III. It helps you design, build, and submit your clinical studies faster. You can store and reuse your standardized metadata such as annotated eCRFs, datasets, and controlled terminology. This increases the quality of your data. And everything’s stored in 1 place.
You can create your datasets upfront. Even before you’ve started collecting patient data! This means you can check your datasets will meet regulatory requirements right at the start. And you get a head start on mapping your ADaM datasets back to SDTM.
Global search functionality lets you find studies, standards, and assets quickly. That means your team has greater control, transparency, and communication. You’ll have higher quality data and it’ll be more consistent for submissions.
CDISC standards are built-in so you’ll automatically comply with FDA and NCI standards.
Automating SDTM and ADaM datasets is quick and easy. No coding’s required and our tools help you match variables in SDTM and ADaM to variables in your source datasets. Once you have everything set up, it’s only 1 click to get your datasets and define.xml.
Our built-in APIs let other systems integrate with Formedix such as from a SAS based environment. And we use external API’s from other systems to integrate with them, such as RAVE AWS API and other leading EDC’s.
So implementing CDISC standards doesn’t need to be a headache! If you want to find out more, you can have your own customized demo. Or you can arrange a call to talk about what you want to achieve and see how we can help.